Table of Contents
- Defining the term ‘empathy burnout’ and its impact on mental health.
- The difference between empathy and sympathy.
- The emotional and physical toll of empathy burnout on individuals
- Causes of empathy Burnout in high-stress jobs and Caregiving roles
- Common signs and symptoms of empathy burnout to look out for
- The Connection between empathy burnout and mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
- The role of social media and technology in exacerbating empathy burnout
- Techniques for improving empathy without sacrificing personal well-being
- The importance of seeking professional help for empathy burnout and other mental health concerns.
- Strategies for organizations and employers to support employees who may be at risk for empathy burnout.
- Frequently Asked Questions

Defining the term ‘empathy burnout’ and its impact on mental health.
1. Empathy Burnout
Empathy burnout is a phenomenon that occurs when individuals experience emotional exhaustion and a reduced ability to empathize with others due to chronic exposure to stress and traumatic events. This can be particularly common among caregivers, healthcare professionals, educators, and those in high-stress professions.
2. The Impact of Empathy Burnout on Mental Health
The impact of empathy burnout on mental health can be significant. It can lead to feelings of depression, anxiety, and detachment from others. Physical symptoms such as fatigue, sleep disturbances, and decreased immune function can also occur.
3. Factors that Contribute to Empathy Burnout
Research has shown that empathy burnout is more likely to occur when individuals are exposed to chronic stress, such as caring for a loved one with a chronic illness or working in a high-pressure job such as nursing. Healthcare professionals, in particular, are at high risk for empathy burnout due to their daily exposure to suffering and pain.
4. Signs and Symptoms of Empathy Burnout
It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of empathy burnout. These can include feeling emotionally drained, irritable, or having difficulty concentrating. Without addressing these symptoms, empathy burnout can lead to negative mental health outcomes.
5. Preventing and Treating Empathy Burnout
To prevent empathy burnout, it is crucial to practice self-care techniques such as engaging in physical activity, meditation, and talking to a therapist. It is also important to set boundaries and take breaks from stressful situations, particularly for those in caregiving and high-stress professions.
Treatment for empathy burnout may include counseling, support groups, and other forms of mental health treatment. It is important to seek help as soon as possible to prevent long-term negative effects on mental health.
The difference between empathy and sympathy.
Empathy and sympathy are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person, while sympathy is feeling concern or pity for someone else’s misfortune. Understanding the difference between these two terms is important in developing strong relationships and promoting mental wellness.
Empathy involves being able to connect with another person’s emotional state. This connection may involve recognizing the emotions that another person is experiencing and being able to understand why they are feeling that way. When a person is empathetic, they are able to put themselves in the shoes of another person and see the situation from their perspective.
On the other hand, sympathy involves feeling concerned for another person’s well-being. While sympathy may involve an emotional response to someone else’s situation, it is not the same as fully understanding and sharing the other person’s emotions.
It is important to note that both empathy and sympathy are important in building strong relationships and promoting mental wellness. Empathy helps individuals to connect with others on a deeper level, while sympathy allows us to feel compassion for others.
Studies have shown that empathy can have a positive impact on mental health. One study found that individuals who scored high in empathy had lower levels of depression and anxiety. Additionally, empathy has been shown to be a key component in promoting social support and reducing feelings of isolation.
While empathy and sympathy are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings. Empathy involves understanding and sharing the emotions of another person, while sympathy involves feeling concerned for another person’s well-being. Both are important in building strong relationships and promoting mental wellness.
The emotional and physical toll of empathy burnout on individuals
1. Understanding Empathy Burnout
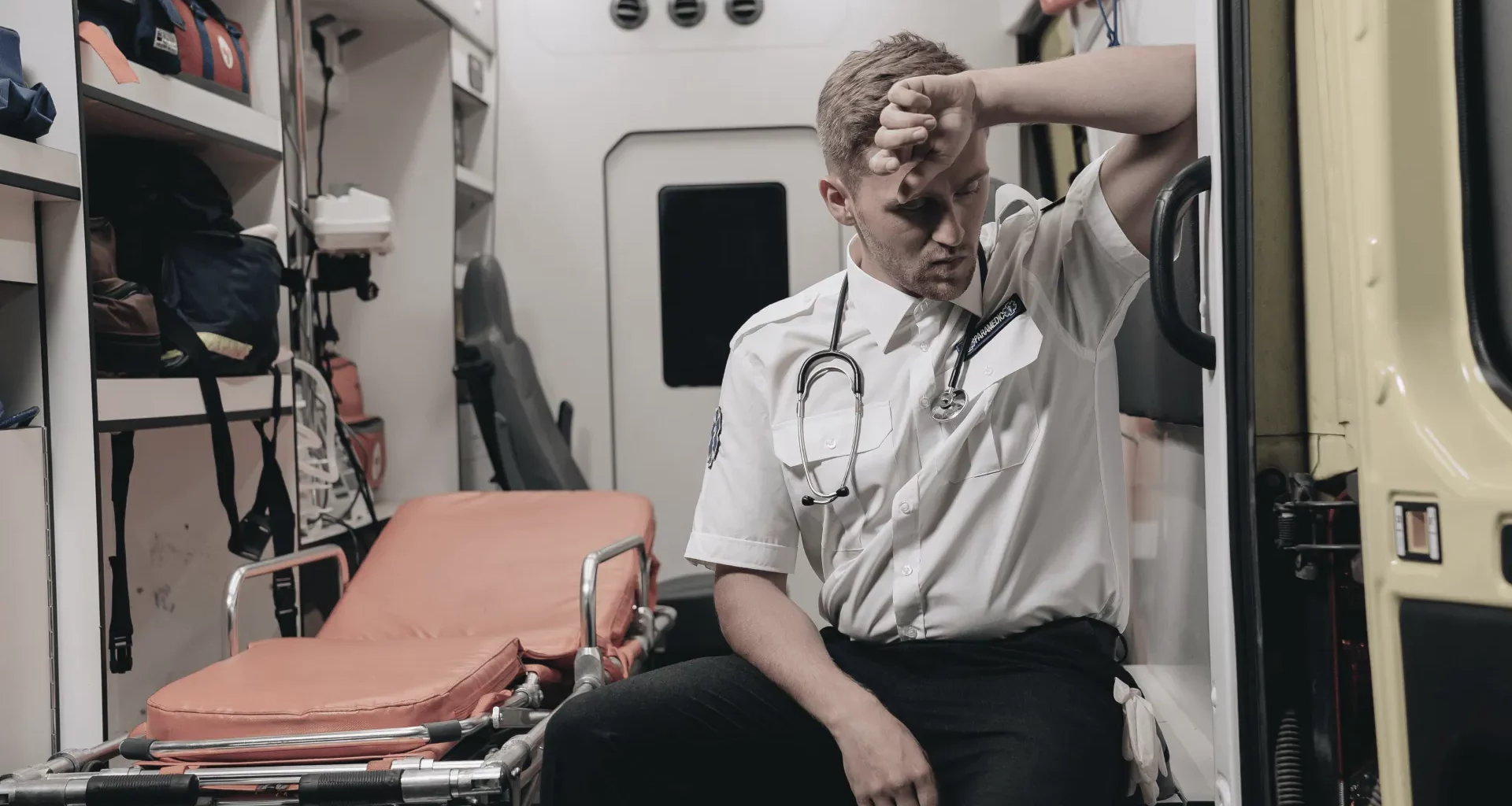
Empathy burnout, also known as compassion fatigue, is a phenomenon where individuals who work in professions that require them to empathize with others experience a gradual depletion of their emotional and physical resources. Empathy burnout is a form of chronic stress that can lead to emotional exhaustion, detachment from others, and a decreased ability to feel empathy. It is often observed in healthcare workers, social workers, first responders, and other professions that require constant emotional labor.
2. Emotional Toll of Empathy Burnout
The emotional toll of empathy burnout can be significant, leading to emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced empathy. Emotional exhaustion is characterized by feelings of being emotionally drained and overwhelmed by the demands of the job. Depersonalization is a detachment from others, a feeling of emotional numbness, and a lack of empathy toward others. Reduced empathy is a decrease in the ability to feel empathy and connect with others emotionally.
Research has shown that empathy burnout can lead to depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in individuals. A study conducted International Journal of Nursing Studies found that healthcare workers who experienced high levels of empathy burnout had a significantly higher risk of developing PTSD symptoms.
3. Physical Toll of Empathy Burnout
The physical toll of empathy burnout can be just as significant as the emotional toll. Chronic stress and emotional exhaustion can lead to physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, insomnia, and gastrointestinal problems. Research has shown that healthcare workers who experience high levels of empathy burnout are at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, and other chronic health conditions.
A study found that physicians who experienced high levels of burnout had a 38% higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
4. Coping with Empathy Burnout
Coping with empathy burnout can be challenging, but there are strategies that individuals can use to help prevent and manage empathy burnout. One effective strategy is self-care, which includes activities such as exercise, mindfulness, and engaging in activities that bring joy and pleasure. Setting boundaries and learning to say no to additional work demands can also help prevent burnout.
5. Seeking Professional Help for Empathy Burnout
If self-care strategies are not effective, seeking professional help may be necessary. Therapists who specialize in burnout can help individuals develop coping strategies and address the underlying causes of empathy burnout. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) are effective therapies for burnout.
Causes of empathy Burnout in high-stress jobs and Caregiving roles
1. High-stress jobs
Individuals who work in high-stress jobs, such as healthcare, social work, and emergency response, are at a higher risk of developing empathy burnout. These jobs require constant emotional labor and can involve exposure to traumatic events.
A study found that pediatric medical oncologists in the United States experienced high levels of compassion fatigue and burnout, which had negative consequences for their well-being and job performance. The study highlights the importance of providing support for healthcare workers to prevent and manage empathy burnout.
2. Caregiving roles
Individuals who assume caregiving roles for family members or friends can also experience empathy burnout. Caregiving can be a demanding and stressful role, and it often involves emotional labor and exposure to others’ emotional pain.
A study found that family caregivers of individuals with dementia experienced high levels of compassion fatigue and burnout, which had negative consequences for their well-being and ability to provide care. The study emphasizes the need for support and resources for family caregivers to prevent and manage empathy burnout.
3. Personal Characteristics
Personal characteristics such as high empathy and perfectionism can also contribute to empathy burnout. Individuals who are highly empathetic may be more susceptible to feeling overwhelmed by others’ emotional pain, while individuals who are perfectionistic may struggle with setting boundaries and managing their workload.
Empathy burnout is a complex phenomenon with multiple causes, including high-stress jobs, caregiving roles, and personal characteristics. By understanding the causes of empathy burnout and implementing strategies to prevent and manage burnout, individuals can continue to provide empathetic care while maintaining their own emotional and physical well-being.
Common signs and symptoms of empathy burnout to look out for
1. Emotional exhaustion
Emotional exhaustion is a feeling of being drained, depleted, or overwhelmed by emotional demands. This can include feeling tired, irritable, or apathetic.
A study found that emotional exhaustion is a common symptom of compassion fatigue, which is a type of burnout that occurs in helping professions. The study emphasizes the importance of recognizing and addressing emotional exhaustion in individuals who work in high-stress jobs.
2. Decreased empathy
Decreased empathy is a common symptom of empathy burnout. This can include feeling numb, detached, or indifferent to others’ emotional pain.
A study found that healthcare workers who experienced burnout had lower levels of empathy than those who did not experience burnout. The study highlights the importance of maintaining empathy as a key component of high-quality healthcare.
3. Physical symptoms
Physical symptoms, such as headaches, stomach problems, and sleep disturbances, can also be a sign of empathy burnout.
A study found that healthcare workers who experienced burnout were more likely to report physical symptoms such as headaches, stomach problems, and sleep disturbances. The study emphasizes the importance of addressing both the emotional and physical aspects of burnout in healthcare workers.
4. Decreased job satisfaction
Individuals who are experiencing empathy burnout may also experience a decrease in job satisfaction. This can include feeling dissatisfied with their work, feeling unmotivated, or feeling like their work is not making a difference.
A study found that burnout was negatively associated with job satisfaction in a sample of Korean nurses. The study emphasizes the importance of addressing burnout in order to promote job satisfaction and well-being among healthcare workers.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of empathy burnout is an important step in preventing and managing burnout. By addressing the emotional, physical, and job-related aspects of burnout, individuals can work to maintain their well-being and continue to provide high-quality care to others.
The Connection between empathy burnout and mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
1. Depression
Depression is a common mental health condition that is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. Empathy burnout can be a contributing factor to depression.
A study found that compassion fatigue, which is a type of burnout that occurs in helping professions, is associated with depression in nurses. The study highlights the importance of addressing compassion fatigue in order to prevent depression among healthcare workers.
2. Anxiety
Anxiety is a mental health condition that is characterized by persistent feelings of worry, fear, and apprehension. Empathy burnout can also contribute to anxiety.
A study found that healthcare workers who experienced burnout were more likely to report symptoms of anxiety. The study emphasizes the importance of addressing burnout in order to promote mental health and well-being among healthcare workers.
3. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
PTSD is a mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Individuals who experience empathy burnout from consistently working with clients who have experienced trauma may be at increased risk for developing PTSD.
A study found that exposure to trauma in helping professions is a risk factor for developing PTSD. The study highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing the impact of trauma exposure in order to prevent PTSD among healthcare workers.
Overall, empathy burnout can have significant consequences on mental health, including the development of depression, anxiety, and PTSD. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of empathy burnout and taking steps to address it, individuals can work to maintain their mental health and well-being
Empathy burnout is a complex phenomenon with multiple causes, including high-stress jobs, caregiving roles, and personal characteristics. By understanding the causes of empathy burnout and implementing strategies to prevent and manage burnout, individuals can continue to provide empathetic care while maintaining their own emotional and physical well-being
The role of social media and technology in exacerbating empathy burnout
1. Continuous Exposure to Emotional Demands
Social media and technology provide constant access to others, which can lead to continuous exposure to emotional demands. This can be particularly stressful for individuals in helping professions or caregiving roles.
A study found that journalists who used Twitter to connect with their audience reported higher levels of burnout. The study highlights the impact of social media on the emotional demands experienced by individuals in high-stress jobs.
2. Reduced Work-Life Boundaries
Social media and technology have also contributed to the blurring of work-life boundaries, making it difficult for individuals to disconnect from work and caregiving responsibilities.
Individuals who had weaker boundaries between their personal and professional lives reported higher levels of burnout.
3. Comparison and Self-Doubt
Social media and technology have also contributed to increased comparison and self-doubt among individuals, which can exacerbate empathy burnout.
A study found that social media use is associated with increased appearance comparison and body dissatisfaction. The study highlights the impact of social media on self-esteem and well-being.
4. Constant Availability
Social media and technology have also created a culture of constant availability, making it difficult for individuals to disconnect and take time for self-care.
A study published in the Journal of Occupational Health Psychology found that individuals who report a lack of recovery from work are at increased risk for burnout. The study highlights the importance of taking time for self-care in order to prevent burnout.
Social media and technology have contributed to the exacerbation of empathy burnout. By recognizing the impact of social media and technology on our well-being and taking steps to manage our use, we can work to prevent burnout and maintain our mental health and well-being.
Techniques for improving empathy without sacrificing personal well-being
1. Self-care
Self-care is essential for mental and physical well-being, particularly for individuals who frequently encounter emotional stress. Taking the time to engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as exercise, mindfulness, or pursuing hobbies, can help manage the emotional weight of empathy.
2. Mindful listening
Mindful listening involves actively focusing on what the speaker is saying, without judgment or interruption. It helps to build a deeper understanding of the speaker’s perspective, without compromising one’s emotional well-being.
3. Boundaries
Setting boundaries is an essential part of protecting one’s emotional and physical health. Individuals can use techniques such as saying “no” and being assertive to protect themselves from overextending their empathetic capabilities.
4. Perspective-taking
Perspective-taking involves the ability to see things from another person’s point of view. It can help individuals to understand another person’s perspective without necessarily adopting their emotional state.
5. Empathy training
Empathy training can involve formal programs or workshops designed to improve empathetic skills. These programs can teach individuals techniques for empathy, including active listening and perspective-taking while providing strategies to manage the emotional impact of empathy.
6. Cognitive reappraisal
Cognitive reappraisal is a technique that involves reframing negative thoughts into more positive ones. It can help individuals to manage their emotional response to empathy without compromising their ability to connect with others.
The importance of seeking professional help for empathy burnout and other mental health concerns.
1. The Benefits of Early Intervention
Empathy burnout and other mental health concerns can have a significant impact on an individual’s life, affecting their personal relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life. However, with early intervention, individuals can learn coping skills, reduce symptoms, and improve their overall well-being. Seeking professional help as soon as possible can help prevent symptoms from getting worse and improve outcomes. According to a study individuals who receive treatment for mental health concerns early on have better long-term outcomes and are less likely to experience relapse. Early intervention can also help prevent more serious mental health concerns from developing, such as major depressive disorder or anxiety disorders.
2. Types of Mental Health Professionals
There are several types of mental health professionals who can provide support and treatment for individuals experiencing empathy burnout and other mental health concerns. These professionals include psychiatrists, psychologists, licensed clinical social workers, licensed professional counselors, and marriage and family therapists. Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health and can prescribe medication to treat mental health conditions. Psychologists are trained to provide psychotherapy and other forms of talk therapy. Licensed clinical social workers provide a wide range of services, including therapy, case management, and advocacy. Licensed professional counselors and marriage and family therapists provide therapy and other mental health services.
3. Finding the Right Provider
Finding the right mental health provider is an essential part of seeking professional help for empathy burnout and other mental health concerns. When looking for a provider, individuals should consider the provider’s credentials, experience, and approach to treatment. It is also important to find a provider who is a good fit for the individual’s needs and preferences. Many mental health professionals offer a free initial consultation, which can help individuals determine if the provider is a good match.
4. Breaking the Stigma Surrounding Mental Health
One of the biggest barriers to seeking professional help for empathy burnout and other mental health concerns is the stigma surrounding mental health. Many individuals may feel embarrassed or ashamed to seek help, leading to delayed treatment and worsening symptoms. However, it is important to remember that seeking help is a sign of strength, and there is nothing to be ashamed of when it comes to mental health concerns. It is essential to break the stigma surrounding mental health and encourage individuals to seek help when they need it.
Strategies for organizations and employers to support employees who may be at risk for empathy burnout.
1. Encourage self-care and work-life balance
Employers can encourage their employees to take care of themselves by providing resources and support for healthy habits. Encouraging breaks, vacations, and time off to recharge can help employees manage stress and avoid burnout.
According to a study, work engagement, which is the opposite of burnout, was positively associated with work-family balance and leisure time. Providing flexible work hours, part-time work, and remote work options can also help employees better manage their work and personal lives.
2. Offer training and support
Employers can provide training on stress management, resilience, and coping strategies to help employees develop the skills they need to manage stress and prevent burnout. They can also offer support, such as counseling or coaching services, to employees who may be struggling with empathy burnout.
A study found that a positive work environment and supportive leadership were associated with lower levels of burnout. Training programs for managers and supervisors can help them recognize the signs of burnout and provide support for their employees.
3. Foster a supportive workplace culture
A supportive workplace culture can help prevent empathy burnout by reducing the stigma around mental health and promoting positive relationships between employees. Employers can encourage open communication, provide opportunities for social support, and offer recognition and appreciation for employees’ hard work.
In a study, social support and recognition were found to be protective factors against burnout in healthcare workers. Encouraging social events, team-building activities, and recognition programs can help employees feel valued and supported.
4. Create a safe space for employees to express concerns
Employers can create a safe space for employees to share their concerns and struggles without fear of retribution. Providing a confidential employee assistance program (EAP) can offer employees the opportunity to discuss their struggles in a confidential setting.
According to a study, EAPs were found to be effective in preventing burnout and improving employee well-being. Providing resources and support for employees who are struggling with empathy burnout can help them feel supported and valued.
Frequently Asked Questions
Anyone who regularly provides care or support to others, such as healthcare professionals, social workers, and caregivers, is at risk of empathy burnout. It can also occur in individuals who have experienced trauma or have a history of mental health issues.
Empathy burnout is not necessarily a form of depression, but it can lead to symptoms of depression such as low mood, loss of interest, and fatigue.
Yes, empathy burnout can be a long-term problem if left untreated. It can lead to chronic stress, emotional exhaustion, and decreased quality of life.
Self-care activities that can help prevent empathy burnout include regular exercise, mindfulness practices, spending time with loved ones, engaging in hobbies or creative pursuits, and taking time off when needed.